The CellVue NIR815 cell labeling kit uses proprietary membrane labeling technology to stably incorporate CellVue NIR815, a fluorescent dye with long aliphatic tails, into lipid regions of the cell membrane1. The labeling buffer provided with the kit (Diluent C) is an iso-osmotic aqueous solution which contains no physiologic salts or buffers, detergents, or organic solvents and is designed to maintain cell viability while maximizing dye solubility and staining efficiency. The labeling efficiency of staining is dependent upon the cell type being labeled and the membranes of the cells2, 3.
NIR Cell Linker Used for Short-term in vitro Studies
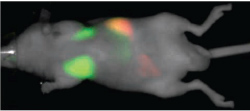
CellVue NIR815 dye has been reported to be useful for short-term in vitro cell proliferation studies4, cell tracking in isolated organ preparation applications5, and cell tracking using the Pearl® Small Animal Imaging System or Odyssey® CLx Imager or Odyssey Classic Infrared Imaging System6.
Kit Components
- CellVue NIR815 dye stock (1 vial containing 0.1 mL, 1 x 10-3 M in ethanol)
- Diluent C (1 vial containing 10 mL, sufficient for 5 labeling reactions)
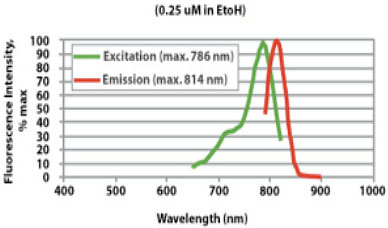
Excitation and Emission Properties of CellVue NIR815 Dye
The excitation and emission properties of CellVue NIR815 dye are compatible with a range of commercially available near-infrared fluorescent plate readers, flow cytometers, in vitro and in vivo fluorescent imaging systems, and confocal microscopes.
Example Data
References
- Horan, P. K., and Slezak, S. E., Nature, 340, 167-168 (1989).
- Horan, P. K., et al., Methods Cell Biol., 33, 469-490 (1990).
- Poon, R.Y., et al. In Living Color: Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Protocols, Diamond, R. A., and DeMaggio, S. (Eds.). p. 302-352 (Springer-Verlag, New York, 2000).
- Stewart, C. C., Woodring, M. L., Podniesinski, E. and Gray, B. D. Flow Cytometer in the Infrared: Inexpensive Modifications to a Commercial Instrument. Cytometry, Part A, 67A, #2, 104-111 (2005).
- Al-Mehdi, A-B, et al. Increased Depth of Cellular Imaging in the Intact Lung Using Far Red and Near Infrared Fluorescent Probes. Int. J. Biomed. Imag., Vol 2006, Article ID 37470, p 1-7.
- Thomas, D. L., et al., Experimental Manipulations of Afferent Immune Responses Influence Efferent Immune Responses to Brain Tumors. Cancer Immunol. Immunother.Sep, 57(9): 1323-33 (2008).
CellVue is a registered trademark of PTI Research, Inc, used under license. CellVue products are sold under license from PTI Research, Inc.. US Patent # 8,029,767B2.
