Printable PDF: Interpreting Diagnostic Values
This content as a pdf that can be saved to your computer or printed.
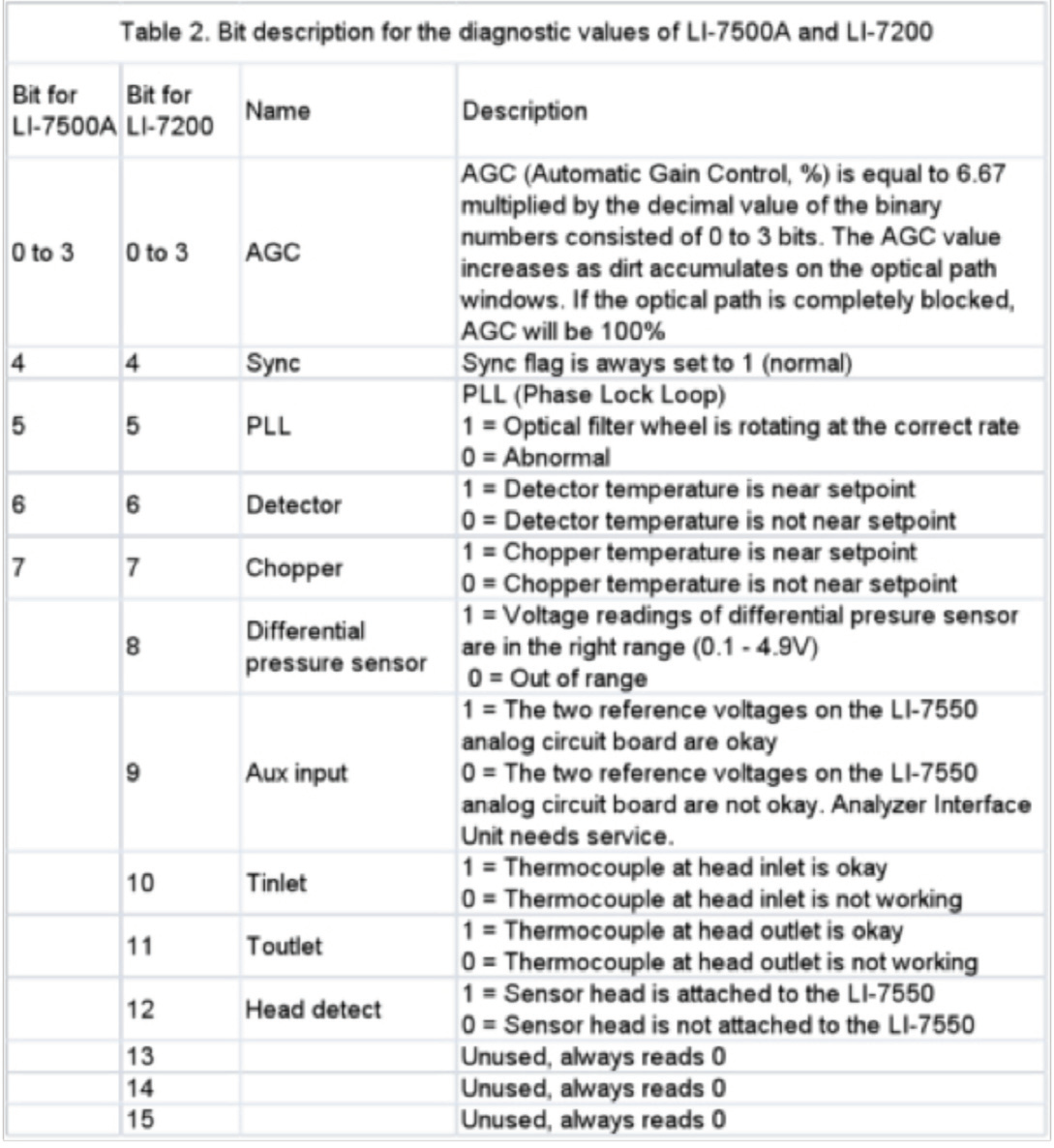
The diagnostic values output by the LI-7500A and LI-7200 CO2/H2O gas analyzers indicate whether or not your instruments are working normally, and what might have gone wrong in case of a malfunction. Here are the two steps for interpreting the diagnostic values:
| Division | Quotient | Remainder |
|---|---|---|
| 254/2 | 127 | 0 |
| 127/2 | 63 | 1 |
| 63/2 | 31 | 1 |
| 31/2 | 15 | 1 |
| 15/2 | 7 | 1 |
| 7/2 | 3 | 1 |
| 3/2 | 1 | 1 |
| 1/2 | 0 | 1 |
Here are two examples showing how to interpret the LI-7500A and LI-7200 diagnostic values:
- A diagnostic value of 254 for an LI-7500A is equal to 11111110 in binary format as shown. From Table 2, the AGC is equal to 6.67 × (1×23 + 1×22 + 1×21 + 0×20) = 93. A high AGC value such as this indicates the LI-7500A is malfunctioning. The optical path is partially blocked. Clean the windows and check if there is anything wrong with the optical path.
- A diagnostic value of 8061 for an LI-7200 is equal to 0001111101111101 in binary format. The AGC is equal to 6.67 × (1×23 + 1×22 + 0×21 + 1×20) = 87. The zero at the seventh bit indicates the chopper temperature controller is out of range, hot or cold. Check that the sensor head cables to the LI-7550 are tight and the chopper temperature is set properly (5 vs 30 °C).