Using the 7900-180 Soil Temperature Sensor in Biomet Systems
Printable PDF: Using the 7900-180 Soil Temperature Sensor in Biomet Systems
(Installing-Soil-Temperature-Probe-12675.pdf)
Download this content as a pdf that can be saved to your computer or printed.
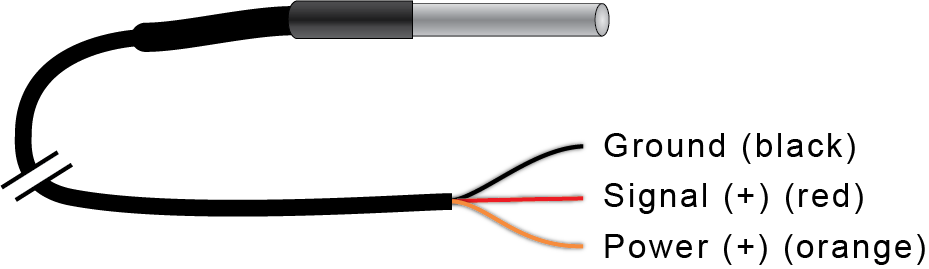
7900-180 Soil Temperature Sensors measure soil temperature and provide that data to a datalogger as analog signals. The 7900-180 sensors are supported by the Basic package (7900-109) and Premium package (7900-119), and custom programs.
| Specifications: | |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range: | -20 to +50 °C |
| Nominal Accuracy: | ±0.25 °C from 0 to +50 °C ±0.30 °C from -20 to 0 °C |
| Probe Diameter: | 4.8 mm (0.190 in.) |
| Probe Length: | 3.8 cm (1.5 in.) |
| Cable Length: | 15 m |
Siting the Soil Temperature Sensors
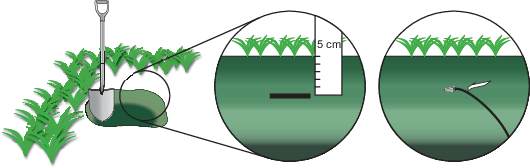
Place the soil temperature sensors in shallow pits near the soil heat flux plates and soil moisture sensors, in minimally disturbed soil that is representative of the site.

Installing the Soil Temperature Sensors
Bury the sensors between 2 and 6 cm deep. Be sure each sensor is completely covered with soil and that there are no air pockets in contact with the sensor. Bury a short length of cable to prevent thermal conduction through the wires. Fill the hole with the excavated soil, matching the bulk density of the soil removed.
Wiring the Sensors to the System
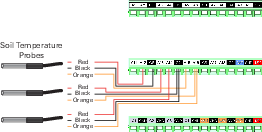
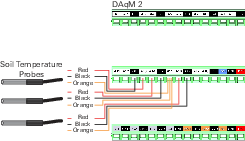
See Figure 1‑1 and Figure 1‑2 for wiring schematics.
| Description | Wire Color | Terminals (7900-109) | DAqM 2 Terminals (7900-119) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal + | Red | A12 | A13 |
| Ground | Black | G6 | G6 |
| Power + | Orange | A15 | A15 |
| Signal + | Red | A13 | A14 |
| Ground | Black | G7 | G7 |
| Power + | Orange | A16 | A15 |
| Signal + | Red | A14 | A16 |
| Ground | Black | G7 | G8 |
| Power + | Orange | A16 | A15 |
Retrieving Data
If the system is configured to log biomet data in .ghg files for processing in EddyPro software or the SmartFlux System, data are stored on the removable USB storage device. Refer to the Biomet Instruction Manual for details.
Maintenance
Soil temperature sensors require little maintenance. Confirm proper operation by examining data. Typically, erroneous data indicates an improperly connected sensor, insecure connections, or a faulty sensor. Check the sensor for proper wiring and secure connections.
